
Those who know little about production agriculture will often ask us why we have a farm safety net in the United States. While there are several justifications to choose from, one of the most notable is that farm policy is designed to help level the playing field for U.S. agricultural producers in the global marketplace. In this article, we illustrate the case of rice.
Rice is an important part of the U.S. agricultural economy, particularly in the South where a number of local communities are highly dependent on the rice industry. Despite its importance, U.S. rice production accounted for just 1.2% of global rice production over the past 5 years. Consequently, the price received by U.S. producers is very much a function of market and political dynamics originating in the rest of the world.
In April 2015, the U.S. International Trade Commission (USITC) reported on the global competitiveness of the U.S. rice industry, concluding that the global rice market was “characterized by significant government intervention in both imports and exports.” One of the most notable serial offenders is India, deploying a cadre of input subsidies and minimum support prices that support their growers to the detriment of producers around the world. In 2020, our own analysis concluded that U.S. rice and wheat farmers were facing almost $600 million per year in lost sales due to the trade-distorting domestic support policies that were being utilized by India (that number rose to $850 million per year in a 2022 update). In February 2024, Rep. Jason Smith, the Chairman of the House Committee on Ways and Means asked USITC to again investigate the global competitiveness of U.S. rice producers. While we won’t prejudge the outcome of their investigation, we can’t help but note that India’s rice exports more than doubled from 2015/16 (when the last USITC report was written) to 2021/22.
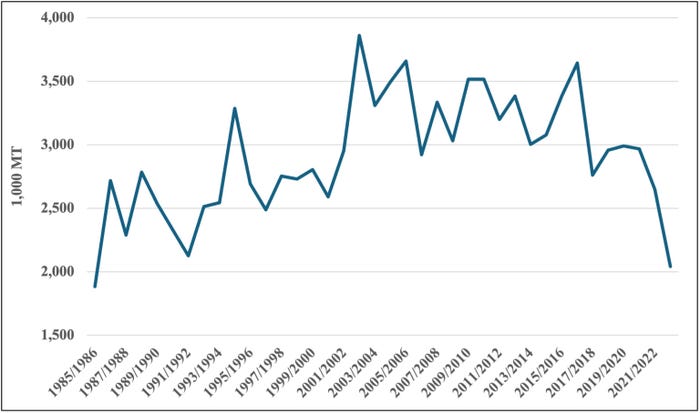
The bottom line is that producers in other markets have significant, government-sponsored benefits that advantage their rice producers over U.S. rice producers. All of this helps to explain why 2022/23 marked the lowest level for U.S. rice exports since 1985/86 (Figure 1). While previous Southern Ag Today articles have explored the temporary reprieve resulting from India’s recent export ban (see here and here), the eventual return to status quo will inevitably result in lower prices for producers around the world, including in the United States.
All of this serves as yet another reminder of the importance of the farm safety net in leveling the playing field for America’s agricultural producers. It also magnifies the importance of updating the farm safety net in the next farm bill to ensure that it is reflective of the risks currently being faced by America’s agricultural producers.
Figure 1. U.S. Rice Exports from 1985/86 to 2022/23.
Source: Southern Ag Today, a collaboration of economists from 13 Southern universities.
About the Author(s)
You May Also Like




