
Sunflower rust could be a problem this year if the weather pattern of frequent rains, heavy dew and moderate-to-warm temperatures continue.
Confection sunflowers are particularly sensitive to rust, but oilseed types can be susceptible as well, according to Sam Markell, North Dakota State University Extension plant pathologist. Yield and quality losses can be very high if an epidemic develops early in the season.
Markell has some tips on scouting for and managing sunflower rust for growers:
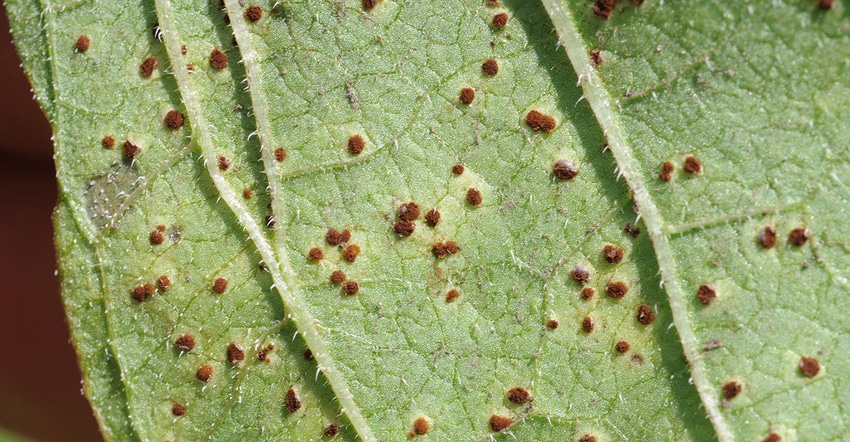
Where to look first. Sunflower rust is commonly first observed near shelterbelts, near last year’s sunflower residue or near wild/volunteer sunflowers.
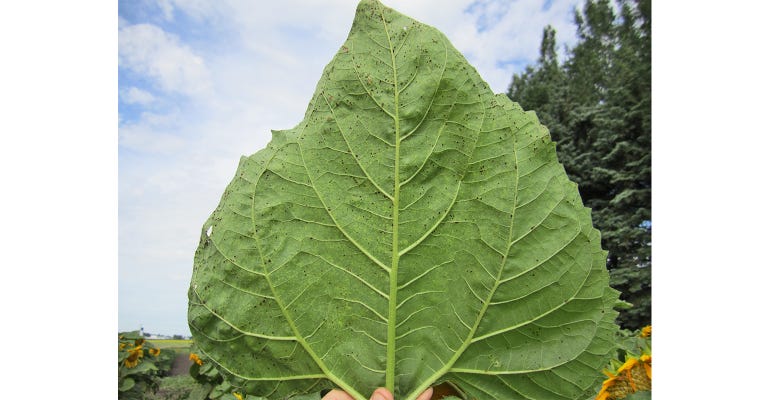 ECONOMIC THRESHOLD: Approximately 1% rust severity can be seen on a fully expanded sunflower leaf.
ECONOMIC THRESHOLD: Approximately 1% rust severity can be seen on a fully expanded sunflower leaf.

What to look for. Rust pustules are cinnamon-brown and dusty, often first found on the leaves in the lower canopy If an epidemic occurs, pustules may be found on stems, petioles and leaves.
What to do, and when. If rust reaches approximately 1% severity on the upper four fully expanded leaves at or before bloom (R5), a fungicide should be considered. At R6 or later (after bloom), fungicide applications have not had impact on yield in out trials.
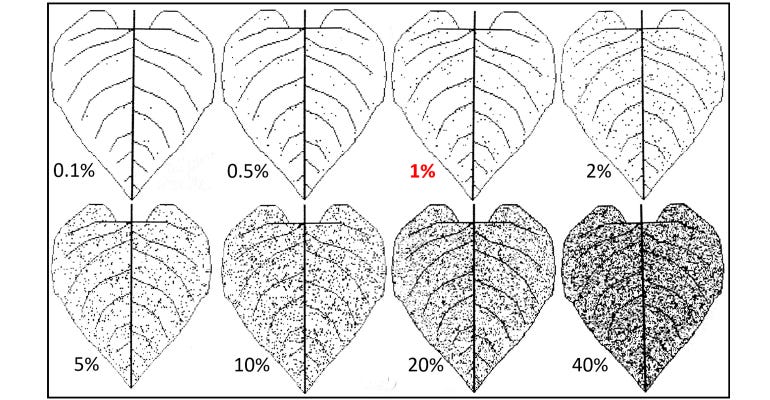 RUST LEVELS: A sunflower rust assessment illustration shows the progress of rust on a sunflower leaf. The level at which fungicide spraying is triggered, 1% severity, is highlighted in red.
RUST LEVELS: A sunflower rust assessment illustration shows the progress of rust on a sunflower leaf. The level at which fungicide spraying is triggered, 1% severity, is highlighted in red.

DeMethylation Inhibitor (DMI) fungicides (FRAC 3: Triazole, tebuconazole, etc..), Qo Inhibitor fungicides (FRAC 11: strobilurins, Headline, Quadris, Aproach) and fungicides containing those modes of actions have been among the most effective on rust in NDSU trials. A FRAC code is a number and letter combination assigned by the Fungicide Resistance Action Committee to group together active ingredients that demonstrate potential for cross resistance.
About the Author(s)
You May Also Like






