April 22, 2024
.jpg?width=850&auto=webp&quality=95&format=jpg&disable=upscale)
At a Glance
- HPAI detected in dairy cattle and poultry in eight states
- Arkansas issues order restricting movement of dairy cattle into state
- No detections in Arkansas since December 2023
As highly pathogenic avian influenza, commonly known as bird flu, is detected in cattle in a growing number of states, the Arkansas Department of Agriculture has issued an order restricting livestock exhibiting symptoms or testing positive for the virus from entering the state.
Dustan Clark, extension poultry health veterinarian for the University of Arkansas System Division of Agriculture, said Arkansas has seen no reports of cattle infected with the virus within its borders. Additionally, there have been no reports of bird flu in Arkansas commercial poultry production facilities or backyard “hobby flocks” since December 2023.
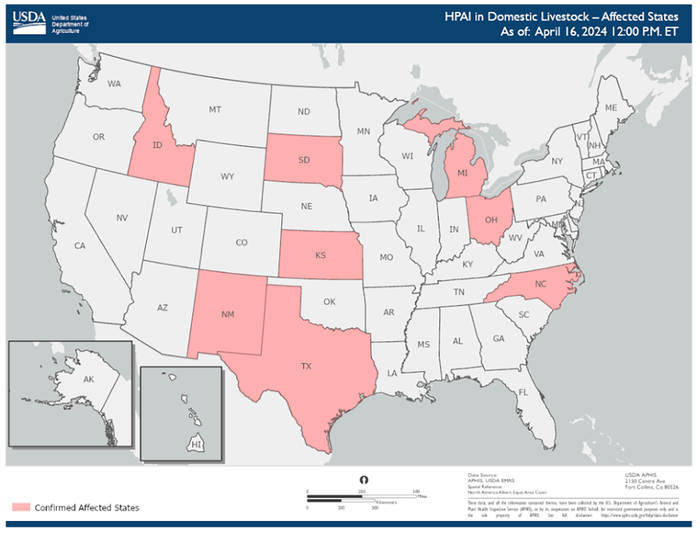
USDA’s Animal and Plant Inspection Service reported confirmed cases of HPAI in cattle in eight states, including Idaho, New Mexico, Texas, South Dakota, Kansas, Michigan, Ohio and North Carolina. All of the reported cases have been in dairy milking cattle. (Image courtesy USDA.)
“So far, we’re doing quite well,” Clark said. “I won’t say we’re safe. We need everyone to maintain good biosecurity practices.”
Clark is also the associate director of the Division of Agriculture’s Poultry Center.
State veterinarian
Per an April 5 letter from Arkansas State Veterinarian John Nilz:
No dairy cattle exhibiting symptoms of or testing positive for HPAI shall be allowed to move into Arkansas.
No dairy cattle from states with impacted herds shall be allowed to move into Arkansas.
Livestock moving into Arkansas found to be in non-compliance with this order shall be quarantined to the nearest facility until all requirements are met on said animals to meet specifications.
“This is still an unfolding issue,” Clark said. As of April 15, USDA’s Animal and Plant Inspection Service reported confirmed cases of HPAI in cattle in eight states, including Idaho, New Mexico, Texas, South Dakota, Kansas, Michigan, Ohio and North Carolina. All of the reported cases have been in dairy milking cattle.
Clark said that since February 2022, more than 90 million birds in the United States have been affected by the H5N1 strain of bird flu.
“It’s been detected in about 480 commercial flocks and 645 hobby flocks,” Clark said.
According to an April 16 U.S. Department of Agriculture report, more than 8.5 million birds had been affected within the previous 30 days. While HPAI has been detected in 48 states over the last two years, it has only been reported in eight states — Michigan, Florida, New Mexico, Minnesota, Kansas, Texas, North Carolina and Maine — during that 30-day period.
“Two of the largest of those were table egg flocks in Michigan,” Clark said. “One with more than 2 million birds, the other slightly less than 2 million birds. Then there was a commercial table egg flock in Texas that was more than 1.8 million birds. Those were the biggest in the last 30 days.”
Biosecurity guidelines
Clark said that while USDA and the state veterinarian outlined clear biosecurity guidelines for
the transportation of poultry for both commercial producers and backyard hobbyists, one factor that can’t be controlled is the presence of wild birds.
“Don’t expose your hobby flock birds to wild waterfowl,” Clark said. “Keep them penned up at this point in time, while the migration is still going on. Don’t let them range and keep them away from water sources that may have had wild waterfowl on them, such as a pond.
“If you go somewhere such as a park and there’s a pond there, stay away from it,” he said. “When you go home, clean and disinfect your shoes and change clothes before you visit your own poultry.”
Many public resources are available to help individuals establish good biosecurity measures and assess the possibility of an infected herd or flock, including the USDA’s HPAI biosecurity factsheet, the Division of Agriculture’s biosecurity resources page and the Arkansas Department of Health’s HPAI page. Individuals who think they may have an infected bird should consult their veterinarian or call the Arkansas Department of Agriculture at 501-823-1746.
Source: University of Arkansas System Division of Agriculture
About the Author(s)
You May Also Like






