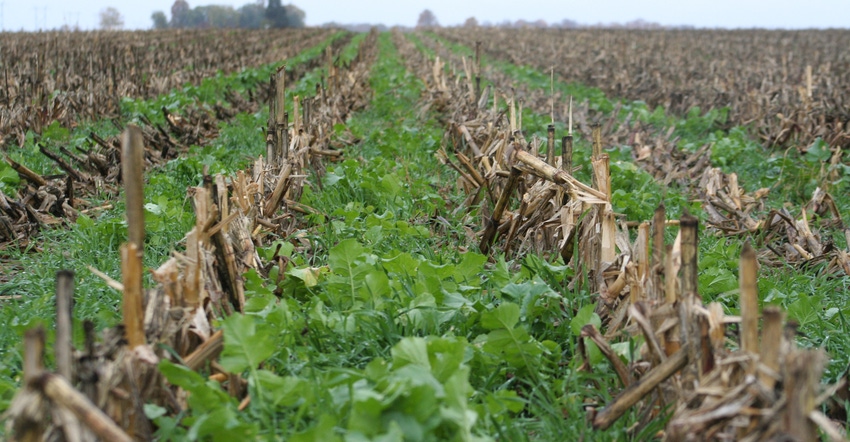
Putting together a list of 10 reasons to grow cover crops is the easy part. The hard part is limiting the list to 10 and not adding more.
This information was prepared by Indiana Conservation Partnership personnel, led by a team of Natural Resources Conservation Service staff. They include Don Donovan, Clint Harrison and Derek Schmitt, district conservationists; Susannah Hinds, grazing specialist; Scot Haley, resource soil scientist; Kris Vance, public affairs specialist; Victor Shelton, state agronomist/grazing specialist; Tony Bailey, state conservation agronomist; and Shannon Zezula, state resource conservationist.
With a new year comes new resolutions. Schmitt provides his set of 10 reasons to consider planting cover crops in fields at or near the end of the 2017 growing season. First, here is a word of caution: Check with your crop insurance and other program agents to ensure cover crops are compatible with your farm’s programs.
1. Cover crops help use moisture. Cover crops can be designed to take up high amounts of moisture to actually help fields dry out for planting in the spring.
2. Cover crops increase water infiltration. Deep-rooting cover crops build organic matter and break through soil compaction layers, increasing water infiltration and reducing ponding on the soil’s surface.
3. Cover crops can suppress weeds. Some cover crops such as cereal rye can help suppress weeds if managed as an integral part of an Integrated Pest Management system.
4. Cover crops can be a source of livestock feed. If managed as part of a prescribed grazing or forage harvest system, cover crops can feed livestock as well as help minimize soil compaction and alleviate other potential issues.
5. Cover crops can feed wildlife. Some cover crops provide direct food resources to wildlife if managed properly. In addition, earthworms and insects that flourish in cover crop fields are excellent food sources for northern bobwhite quail and other bird species.
6. Some cover crop species fix nitrogen in the soil. Legume cover crops will fix nitrogen for next year’s production crop. Just be aware it may take time before the decaying cover cop returns that N to the soil.
7. Other cover crops scavenge for existing nitrogen in the soil. Deep-rooting cover crops gather nitrogen from deep in the soil profile and release the N in the rooting zone as plants decay. This N becomes available for future crops.
8. Cover crops can reduce soil erosion. Coverage of the soil provided by cover crops reduces both wind and water erosion.
9. Cover crops recycle nutrients within the soil. Living plants are crucial to the nutrient cycle. Soil biology is driven by living plants. A field with good nutrient cycling will build soil organic matter.
10. Cover crops build organic matter. Use the full growing season to harvest sunlight to build organic matter over time.
Contact your local USDA Service Center for more information regarding cover crops.
About the Author(s)
You May Also Like