August 15, 2017

By Rick Koelsch
Charles Wortmann and Dan Walters, faculty in the University of Nebraska-Lincoln Department of Agronomy and Horticulture, provide several important insights in a field research initiative that monitored soil erosion, runoff and phosphorus loss from replicated field plots over three cropping seasons immediately after manure application and for four subsequent years when no manure was applied.
This research demonstrates that manure has significant value for reducing runoff and erosion.
By itself, it can't solve the soil erosion, but when used in combination with other soil management practices, manure can protect our soils and limit agriculture's environmental costs. In some instances, however, manure can be an environmental negative if phosphorus is allowed to accumulate in soils. To achieve the environmental benefits of manure and minimize the risks, manure application rates and frequency of re-application to the same field must maintain soil phosphorus (P) levels near the agronomic levels required by the selected crops.
Wortmann and Walters's primary intent was to understand P losses from manure application; however, they also observed several important impacts on soil physical and chemical characteristics. A low and high P composted beef manure was applied to replicated runoff plots (measuring 12 by 36 feet) with a median slope of 5.5% and soil series of Pohocco silt loam. Manure was applied to meet crop nitrogen requirements for three years in a row. Runoff plots were evaluated for these three cropping seasons immediately following manure application, as well as three additional cropping seasons with no manure application. All erosion, runoff and P loss resulting from natural rainfall and pivot irrigation was quantified from March through August of each of the six cropping seasons.
Lessons learned
The research found the following results:
• Compost application reduced erosion and runoff by about two-thirds during the three cropping seasons following manure application (green bars in chart below). Improvements in soil’s water-holding capacity and soil infiltration rates were responsible for the lower runoff and erosion levels. One would expect less total sediment, nitrogen and pesticide levels reaching nearby surface water based on these results. However, increased P levels in neighboring surface waters are an expected negative environmental impact.
• Manure application’s residual benefit for runoff and erosion persisted for at least the next three cropping seasons (blue bars in chart below). This research observed approximate reductions in runoff of 40% and erosion of 55%. The reduced runoff also suggests additional soil moisture storage and greater crop resiliency to dry periods.
• Additional soil quality benefits were observed for soil bulk density, soil organic matter and pH. Although visual evidence of compost disappeared within one year, soil organic matter content and pH benefits of manure were observed four years after the last manure application.
• Increased soil P levels were significant as a result of three consecutive years of compost manure application and producing increased P movement in runoff and erosion. Application to meet crop N requirements applies more P than is required for crop production. Repeating this practice three years in a row, in addition to applying a high P compost (manure from cattle fed diet with distillers grains), further aggravates this negative environmental impact.
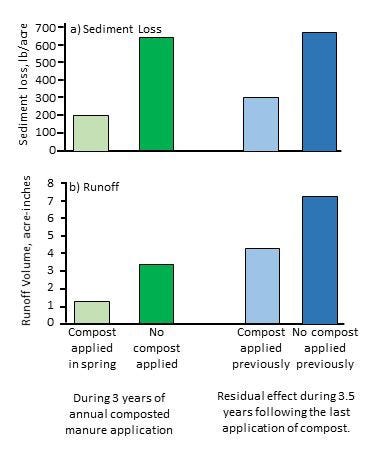 Application of beef manure had produced runoff and erosion benefits during the cropping seasons immediately following manure application (green bars) and for three additional crop years (blue bars) after the last manure application. (Source: Heartland publication RP187, Agricultural Phosphorus Management and Water Quality in the Midwest)
Application of beef manure had produced runoff and erosion benefits during the cropping seasons immediately following manure application (green bars) and for three additional crop years (blue bars) after the last manure application. (Source: Heartland publication RP187, Agricultural Phosphorus Management and Water Quality in the Midwest)

If manure is to be applied at a nitrogen-based rate, it is desirable both economically and environmentally to not reapply manure to the same field until soil P levels return to a level requiring additional P supplementation. For some manures with a low N-to-P ratio, it may be desirable to apply manure at a rate equal to the P removed by the next three to five cropping seasons and then supplement with commercial nitrogen fertilizer to meet crop N requirements. This strategy will produce economic and environmental value, while minimizing the P impact on local surface water.
Manure's economic and soil improvement benefits should both be recognized and built into successful cropping systems.
Koelsch is a livestock environmental Engineer at the University of Nebraksa-Lincoln. This report comes from UNL CropWatch.
You May Also Like