June 9, 2021

Growing vegetables in containers is an activity that can bring families joy and the reward of enjoying fresh, tasty vegetables from right outside the door, Shaun Francis, Extension horticulture specialist for the University of Arkansas at Pine Bluff said.
“Creating a container garden is an easy way of raising some of your favorite vegetables, and it allows you to save money by not having to buy certain produce at the grocery store,” he said. “You can grow just about any vegetable in a container as long as the growing conditions allow. Among the vegetables that lend themselves particularly well to container gardening are tomatoes, peppers, eggplant, beans, lettuce, squash, radishes, carrots, cucumbers and a wide variety of herbs.”
Individuals do not need a plot of land to grow vegetables in containers – a container garden can be located in a number of places, including the front porch or back patio. However, most vegetables perform best when they are exposed to the maximum amount of light throughout the day. The size of the garden can be easily expanded by adding more containers.
And as opposed to a regular garden, container gardens are portable and can be moved to different locations. It also allows individuals to overcome poor soil conditions and avoid weeds and soil-borne diseases.
“Growing vegetables in containers makes it easier for people with physical disabilities to reach and tend to the plants,” Francis said.
Choose a location
Francis said a container garden can be located almost anywhere – on a patio, balcony, rooftop or even in an alleyway.
Since most vegetables need at least six hours of sunlight each day, it is best to choose a sunny location. If the location gets insufficient sunlight, you may need to move the containers during the day or throughout the season as the angle of sunlight changes. On the other hand, it may also be necessary to provide shade for the plants on afternoons during the hottest parts of summer.
“If you are in an overly windy location, you may need to provide some type of wind block as strong winds can topple containers and shred leaves or dislodge fruits from the plants,” he said. “The wall of a building or portable fencing can serve as ideal windbreaks. For plants such as cucumbers that require the use of a trellis or some other type of support, ensure the containers are secured to a fixed structure to prevent them from blowing over.”
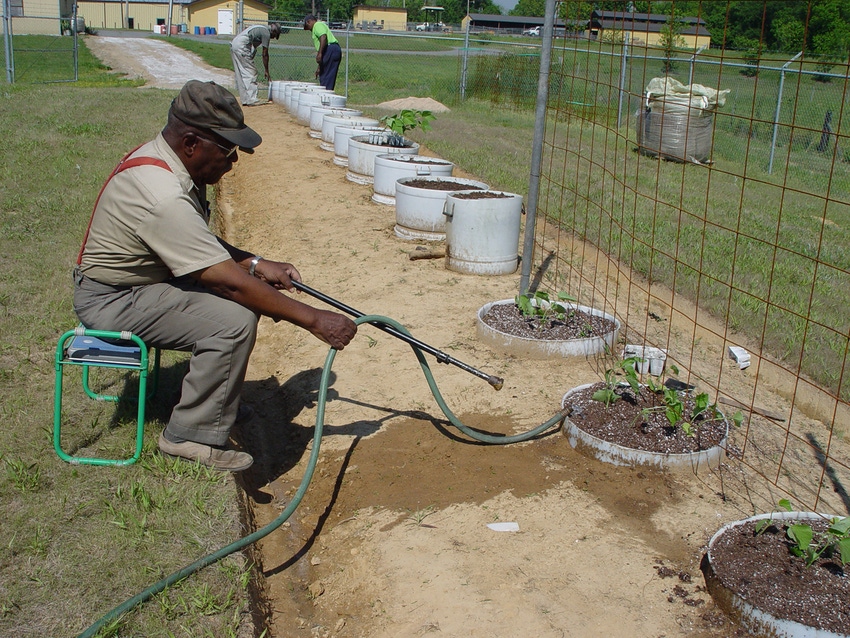
Container
Container must be large enough to hold plants that are fully grown. (University of Arkansas, Pine Bluff)
Just about anything that holds soil can be used as a container for a vegetable garden. However, regardless of the shape, size, color or material, it must be big enough to hold the plants when they are fully grown, have adequate holes to drain excess water and be made of food-safe material. Some of the items that can be used are flowerpots, buckets, wire baskets, bushel baskets, wooden boxes, wooden or plastic barrels, washtubs, grow bags and troughs.
Avoid using treated wood to make your containers as it may contain harmful chemical compounds that could be leached into the soil and absorbed by the vegetable plants. Also, if recycled containers are being used, they must be clean to prevent them from leaching any harmful chemicals into the soil. Metal and dark colored containers should be avoided in hot climates. Black plant pots in particular absorb heat when exposed to the sun and can make the soil too hot for some vegetable plants.
Choose the size of the container according to the crop that will be grown and available space. Larger containers are preferred because they hold more soil, which means they hold moisture longer. Smaller containers tend to dry out faster and may need to be watered more often.
“Remember to use larger, heavier pots for plants such as tomatoes and cucumbers that do better if provided with a support structure,” Francis said. “This minimizes the risk of the support structure tipping over the pot.”
Growing medium
The best medium for growing vegetables in containers is one that holds moisture and nutrients but drains well and provides good air flow. Many types of potting mixes are usually available at local plant nurseries and garden centers. These are ideal for container gardening as they are lightweight and do not compact. They provide adequate drainage and aeration and are usually sterile (lacking diseases and insect pests).
“There are also benefits to creating your own growing medium,” Francis said. “Blending your own vegetable container garden mix using soil, compost and some potting mix can result in huge savings.”
Seeds or seedlings
While it is cheaper to grow vegetables from seeds, it is much easier and more convenient to establish a garden by purchasing seedlings. This is because they are already hardened or acclimatized to the outdoor conditions and it is not necessary to go through the ordeal of nurturing them from the germination to seedling stage.
“Once your container garden is established, check the plants regularly, removing pests and weeds that appear,” Francis said. “Make watering a priority as your containers can dry out rapidly on hot, sunny days. During these periods, you may need to water as often as twice per day. Avoid waiting until plants begin to wilt before watering.”
Source: University of Arkansas, Pine Bluff, which is solely responsible for the information provided and is wholly owned by the source. Informa Business Media and all its subsidiaries are not responsible for any of the content contained in this information asset.
You May Also Like