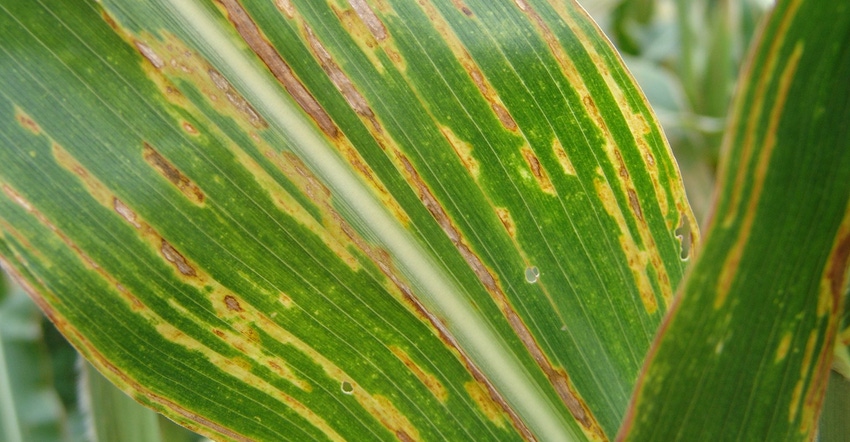
Bacterial leaf streak was found in corn in South Dakota in 2016. Under favorable weather conditions, bacterial leaf streak can get bad enough to reduce yields, says Emmanuel Byamukama, South Dakota State University Extension plant pathologist.
The bacteria Xanthomonas vasicola pv. vasculorum (Xvv) causes bacterial leaf streak. There’s evidence the bacteria can survive on corn residue. In South Dakota, bacterial leaf streak has been found on volunteer corn in a field that had previously been diagnosed with the disease, indicating that it does overwinter. Also, research in Nebraska indicates bacterial leaf streak will likely be found in irrigated corn on corn.
Each year, the weather plays a big role in the development of bacterial leaf streak. Wind, heavy rain and hail increases the risk of the disease. Susceptibility of the hybrids may also play a role, but screening for hybrid resistance or tolerance is not common, Byamukama says.
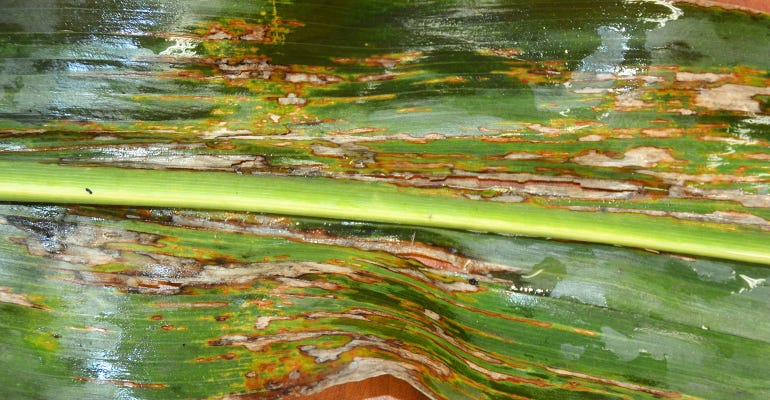 BAD CASE: Advanced symptoms of bacterial leaf streak on corn.
BAD CASE: Advanced symptoms of bacterial leaf streak on corn.

Bacterial leaf streak lesions start as narrow yellow, tan, brown or orange streaks between the leaf veins. They first appear near the midrib, but sometimes can develop anywhere on the leaves. As the symptoms progress, lesions get longer and come together to form larger masses.
Distinguishing bacterial leaf streak and gray leaf spot
Be sure properly diagnose bacterial leaf streak. It looks a lot like gray leaf spot, another corn leaf disease.
There are two differences to look for when trying to distinguish between bacterial leaf streak and gray leaf spot:
1. Consider the time of year when symptoms develop. If symptoms first developed in June, it is likely bacterial leaf streak. Cool weather is not often favorable for gray leaf spot development.
2. Examine the margins of the leaf lesions. Bacterial leaf streak lesions typically have wavy margins. Gray leaf spot lesions have smooth, linear markets.
Be sure to look at many lesions on several plants. Submit leaf samples to a plant lab if you are unsure of the diagnosis or if you suspect bacterial leaf streak has developed in a new area.
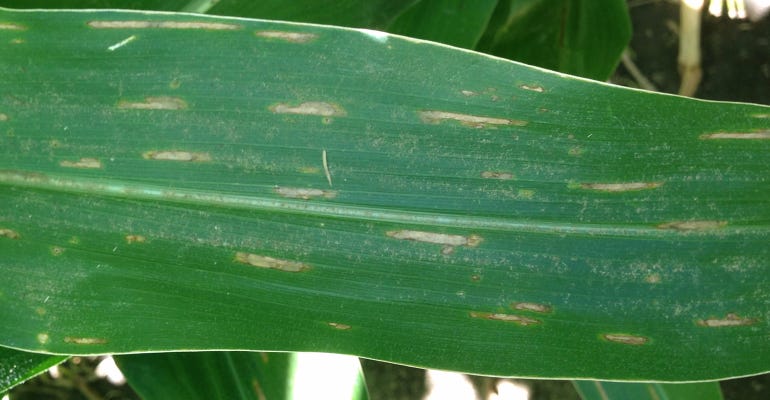 NOT THIS: Gray leaf spot symptoms on a corn leaf. It’s important to know the difference between gray leaf spot and bacterial leaf streak. One can be treated with fungicide, the other cannot.
NOT THIS: Gray leaf spot symptoms on a corn leaf. It’s important to know the difference between gray leaf spot and bacterial leaf streak. One can be treated with fungicide, the other cannot.

A fungicide can help control gray leaf spot, which is caused by a fungus. But a fungicide will not affect bacterial leaf streak, which is caused by bacteria. Tillage and a longer crop rotation can help reduce bacterial leaf streak inoculum levels.
“Like any other bacterial disease, once symptoms develop there is little that can be done to control it in the field,” Byamukama says, “but you can take steps to reduce the risk of having a problem next year.”
About the Author(s)
You May Also Like