August 6, 2018

Source: University of Nebraska-Lincoln
This article summarizes the simulated crop stages and yield forecasts performed on August 1 for 41 locations across the US Corn Belt; the data can be viewed here. Details on the underpinning methodology to simulate phenology and forecast end-of-season yields, as well as on interpretation and uses of yield forecasts, are described in a previous article.
During the last three weeks, air temperature tended to be near or below (Indiana and Nebraska) the historical average, contrasting the very high air temperatures during the previous month as reported in our last article. In the case of rainfall, most locations exhibited near-normal rainfall, except for Iowa and portions of Illinois and Ohio which had below-normal rainfall and some sites in Nebraska and Kansas with above-normal rainfall. A summary of weather conditions during the last two weeks is shown in Figure 1.
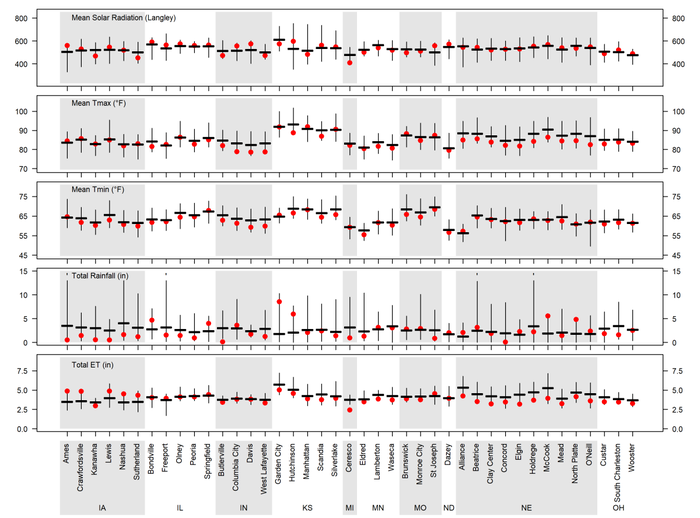
Figure 1. Daily solar radiation, maximum and minimum air temperature (Tmax and Tmin), total rainfall, and total reference grass-based evapotranspiration (ET) for July 11-31, 2018. Vertical bars indicate the range for these variables based on 20+ years of weather records. The horizontal thick line indicates the long-term average and the red dots indicate the 2018 values.
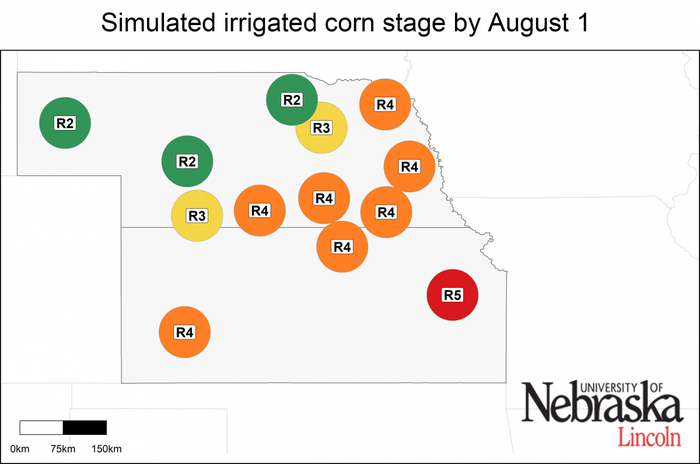
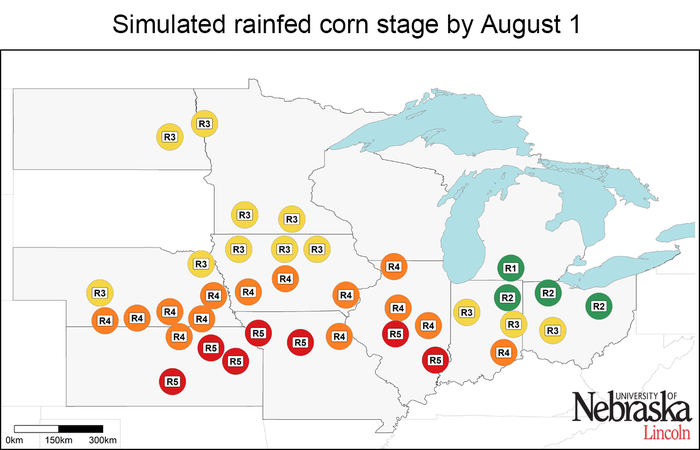
Simulated corn stage across 41 locations
Corn has reached kernel milk stage in most parts of the Corn Belt, except the eastern region where it is still in silking and blister stage. As forecasted in the previous article, sites in the southern fringe of the region (Missouri, Kansas, and southern Illinois) are well ahead of the rest of the locations (Figure 2). They are already in the kernel dent stage and expected to mature within the next two weeks (Figure 3).
High temperatures have accelerated corn development across the entire region. This is reflected in Figure 3, showing the high probability of earlier occurrence of physiological maturity (black layer stage) relative to the long-term average. For example, there is a high probability (>75%, that is, a chance of three out of four) of reaching physiological maturity at least one week earlier in about 75% and 70% of the rainfed and irrigated sites, respectively. This pattern is more pronounced in eastern Kansas, Iowa, and the northern fringe of the region where most sites are expected to reach black layer more than two weeks earlier than average.
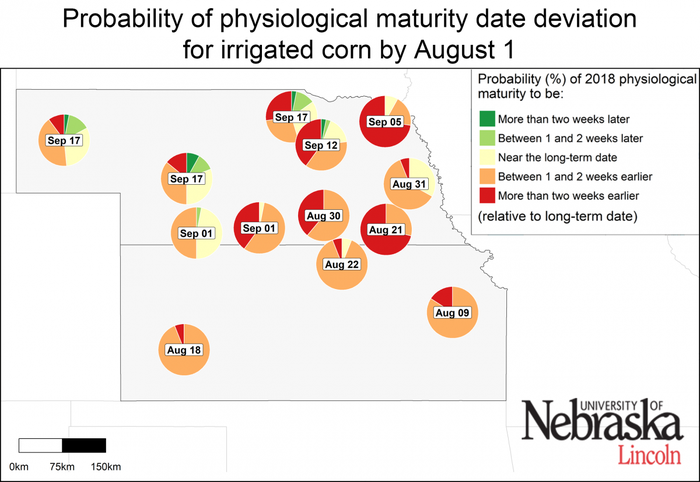
Figure 3. Probability of the 2018 physiological maturity (“black layer”) to be earlier, near, or later than the long-term (2005-2017) average date at each location. Date shown inside the pie chart indicates the 2018 forecasted physiological maturity date if average weather conditions occur from now until the end of the crop cycle. Separate maps are shown for irrigated corn and rainfed corn. The larger a color section is within the pie chart, the higher the probability that end-of-season corn physiological maturity will fall in that category.
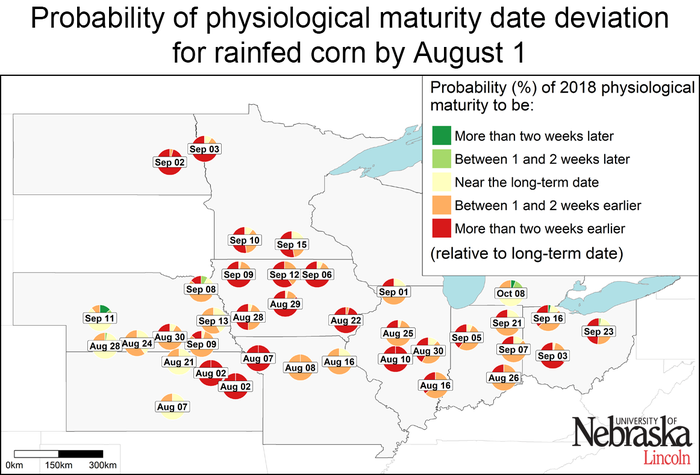
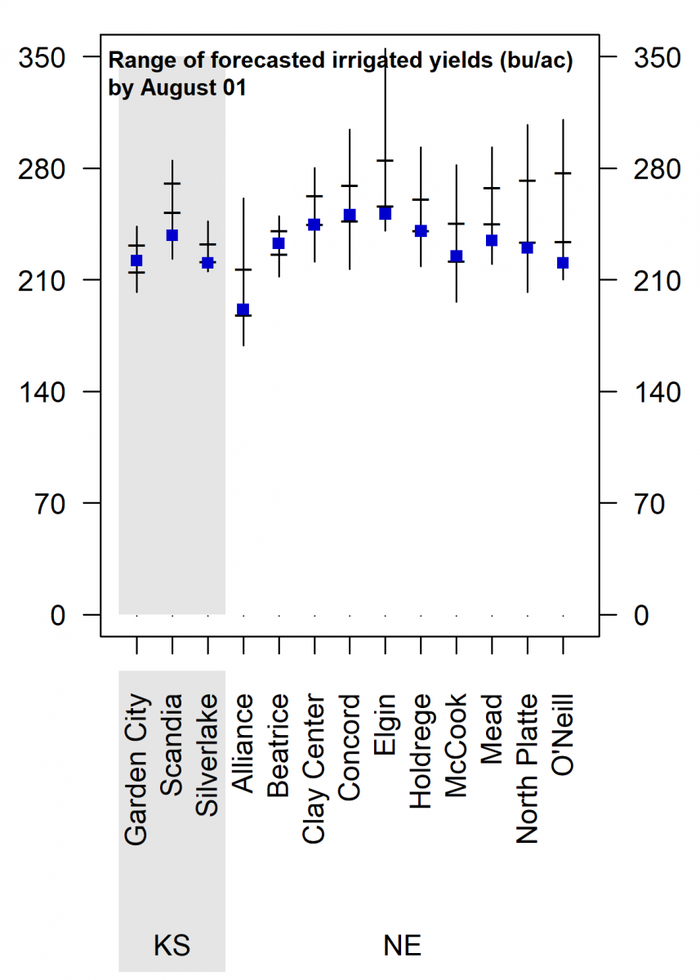
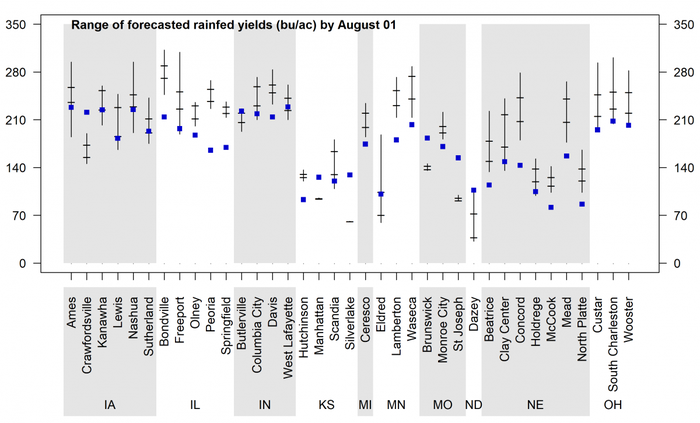
Figure 4. Vertical lines indicate the range of forecasted 2018 corn yield potential as of July 31, based on average planting date in 2018 at each location. Horizontal lines indicate the 25th and 75th percentiles of the yield distribution (associated with respective adverse and favorable weather scenarios during the rest of the season). The blue squares indicate the long-term (2005-2017) average yield potential at each location. Separate charts are shown for irrigated corn and rainfed corn.
Irrigated corn: High probability of near-average yields
The range of forecasted irrigated corn yield potential for each location, as well as the probabilities for yields above, near, or below average, are shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5. About half of the irrigated sites exhibit a high probability (>75%) of above-average yield potential. Favorable weather during the rest of the season that results in a long grain-filling period increases the likelihood of above-average yield. The chance of below-average yield is very low across all irrigated sites.
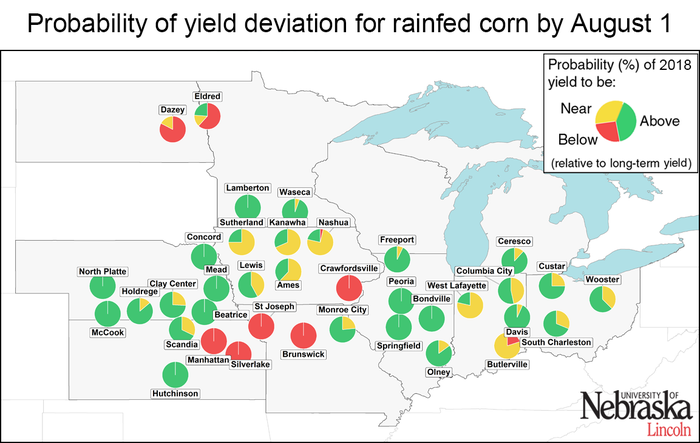
Rainfed corn: Crop cycle shortening is expected to reduce corn yield in the southern and northern regions
Forecasted yield potential is highly variable across rainfed sites (Figures 4 and 5). There is a high probability of above-average yield (>75%) at about half of the sites, mostly located in Nebraska (six sites), Illinois (five sites), and southern Minnesota (two sites). In contrast, there is a high probability of below-average yield for six sites located along a transect that includes portions of northeastern Kansas (Manhattan and Silverlake), northern Missouri (St. Joseph and Brunswick), and southwestern Iowa (Crawfordville). Yield is also forecasted to be below average at the North Dakota site (Dazey). Near-average yields are likely (>75% probability) at two sites in Indiana (Butlerville and West Lafayette) and one site in Iowa (Nashua). The scenario is less clear for the other rainfed sites, although, for most of these sites, the chance of below-average yields is very low.
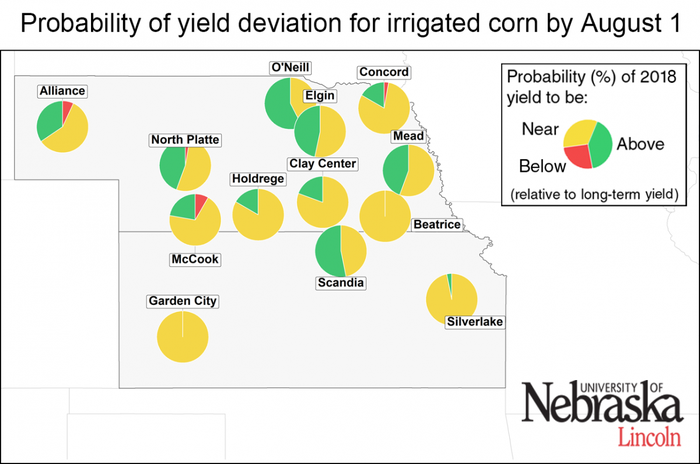
Figure 5. Probability of the 2018 yield potential to be below (<10%, red color), near (± 10%, yellow color), and above (>10%, green color) the long-term (2005-2017) average yield potential at each location. Separate maps are shown for irrigated corn and rainfed corn. The larger a color section is within the pie chart, the higher the probability that end-of-season corn yield will be in that category.
Conclusions
High temperatures during earlier crop stages has hastened corn development. Corn is expected to reach black layer one to three weeks earlier than normal across most locations. Corn in most part of the region has already reached the milk stage and corn in the southern region is expected to mature within the next two weeks. For irrigated corn, there is a high probability of near-average yields for the majority of the sites.
For rainfed corn, the scenario varies across the Corn Belt, with above-average yield expected for 17 locations, mostly located in Nebraska, southern Minnesota, and Illinois. In contrast, six sites in Kansas, Missouri, Iowa, and North Dakota have a high probability of below-average yields. Two sites in Indiana have a high probability of near-average yields. The temperature during the rest of August will likely determine the trend for the other rainfed sites.
These forecasts do not take into consideration problems with stand emergence, hail/flooding damage, replanting, disease, or nitrate leaching. In fields negatively affected by these constraints, actual yields will be lower than estimates provided here. It is important to keep in mind that yield forecasts are not field specific and, instead, represent an estimate of average on-farm yield for a given location and surrounding area in absence of the yield-reducing factors mentioned here. Likewise, crop stages and forecasted yields will deviate from those reported here in fields with planting dates or hybrid maturities that differ markedly from those used as the basis for these forecasts.
Originally posted by the University of Nebraska-Lincoln.
You May Also Like




